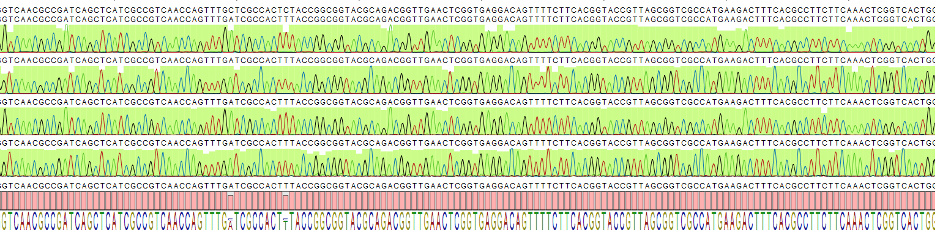
Genome sequencing aims at the determination of the DNA sequence of a complete genome or its selected regions from an organism. In the case of de novo sequencing, the genome sequence is assembled from the sequence reads without prior knowledge about the sequence. In the case of re-sequencing, the reads are aligned and compared to a de novo assembled reference sequence then the structural variants (single nucleotide polymorphism or SNPs, deletions, insertions, rearrangements) are identified. Targeted re-sequencing strategies provide an efficient method to analyse genomic regions, such as the exome (all the exon sequences of a genome), or specific genes of interest a highly parallel way.