Seqomics Ltd. offers a number of ways to trim your sequence reads prior to assembly and mapping, including adapter trimming, quality trimming and length trimming. For each original read, the regions of the sequence to be removed for each type of trimming operation are determined independently according to choices made in the trim dialogs. The types of trim operations that can be performed are:
- Quality trimming based on quality scores
- Ambiguity trimming to trim off e.g. stretches of Ns
- Adapter trimming
- Base trim to remove a specified number of bases at either 3' or 5' end of the reads
- Length trimming to remove reads shorter or longer than a specified threshold
The trim operation that removes the largest region of the original read from either end is performed while other trim operations are ignored as they would just remove part of the same region.
The report includes the following:
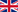
- Trim summary.
- Name. The name of the sequence list used as input.
- Number of reads. Number of reads in the input file.
- Avg. length. Average length of the reads in the input file.
- Number of reads after trim. The number of reads retained after trimming.
- Percentage trimmed. The percentage of the input reads that are retained.
- Avg. length after trim. The average length of the retained sequences.
- Read length before / after trimming. This is a graph showing the number of reads of various lengths. The numbers before and after are overlayed so that you can easily see how the trimming has affected the read lengths (right-click the graph to open it in a new view).
- Trim settings A summary of the settings used for trimming.
- Detailed trim results. A table with one row for each type of trimming:
- Input reads. The number of reads used as input. Since the trimming is done sequentially, the number of retained reads from the first type of trim is also the number of input reads for the next type of trimming.
- No trim. The number of reads that have been retained, unaffected by the trimming.
- Trimmed. The number of reads that have been partly trimmed. This number plus the number from No trim is the total number of retained reads.
- Nothing left or discarded. The number of reads that have been discarded either because the full read was trimmed off or because they did not pass the length trim (e.g. too short) or adapter trim (e.g. if Discard when not found was chosen for the adapter trimming).
Figure 1. A report with statistics on the trim results.
(Source: https://www.qiagenbioinformatics.com)